Earthquakes come and go, often leaving destruction behind. What they luckily don’t usually do is turn around immediately and come back for another push. Except … it looks like they can do it on very rare occasions.
In a new study, scientists have uncovered evidence of an unusual and almost unprecedented boomerang earthquake that shook the deep seafloor under the Atlantic Ocean in 2016.
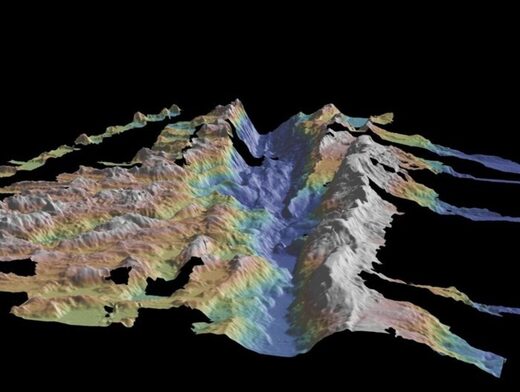
This earthquake, dubbed “reverse super-shear rupture”, occurred along the Romansh fracture. It is an area that lies near the equator, about halfway between the east coast of Brazil and the west coast of Africa.
The rift, which stretches about 900 kilometers between the South American and African tectonic plates, adjacent to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, caused a 7.1 magnitude earthquake in August 2016, which was detected by underwater seismometers in the region, as well as by remote monitoring stations.
Analysis of the signals reveals that this was not an ordinary earthquake, but a strange earthquake that went one way before turning around and returning and with a significant increase in speed.
“While scientists have found that this reverse rupture mechanism is possible on the basis of theoretical models, our new study provides some of the clearest evidence that this mysterious mechanism actually occurs,” Stephen Hicks said, lead researcher and seismologist of Imperial College London.
According to the analysis of seismic data, the 2016 earthquake had two separate phases.
First, the rip extended upward and eastward towards the weak point where the rip zone meets the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Then, in a sudden U-turn, an “unusual westward propagation” occurred, with the tremors returning to the center of the fault and at significantly accelerated “super-shear” velocities of up to 6 kilometers per second.
“Even though the structure of the fault appears to be simple, the quake grew differently, and it was completely the opposite of how we expected the quake to look before we started analyzing the data.”
While the team’s explanation for how this boomerang unfolded remains speculative so far, the researchers speculate that the first, deep phase of the quake released enough fracture energy to initiate a reversal of the rift in the shallower, western underwater terrain.
“Either both sections of the fault were preseismically loaded enough to promote seismogenic failure, or the deeper SE1 fracture instantly increased static stress, immediately causing the shallower portion of SE2 to collapse,” the authors explain in their paper.
Although earthquakes propagating in the opposite direction have been studied by seismologists before, so far there has been little evidence of their existence, and this phenomenon is mainly observed in theoretical modeling.
Finding this type in the real world – in the middle of the ocean – is the first of its kind, not to mention the boomerang that returned at super shear speed.
“To my knowledge, this is the first time this has been reported,” geophysicist Yoshihiro Kaneko of GNS Science in New Zealand, who was not part of the research team, told National Geographic.
The results are reported to Nature Geoscience.